Amorphous and Crystalline Solids
Amorphous and Crystalline Solids: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Amorphous Solids, Crystalline Solids, Distinction between Crystalline and Amorphous Solids and, Types of Solids on the Basis of Nature of Arrangement of Lattice Points
Important Questions on Amorphous and Crystalline Solids
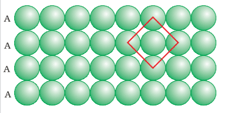
The above diagram is planar. It is a diagram of 2-D _____ close packing.
Which of the following is an amorphous solid?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a crystalline solid?
Classify the following solid as ionic, metallic, molecular network or amorphous.
Plastic
What makes a glass different from a solid such as quartz? Under what conditions quartz could be converted into glass?
Refractive index of a solid is observed to have the same value along all dissections. Comment on the nature of this solid. Would it show cleavage property?
Why a glass considered a super cooled liquid?
Classify the following as amorphous or crystalline solids :
Polyurethane, naphthalene, benzoic acid, Teflon, potassium nitrate, cellophane, polyvinyl chloride, fibre glass, copper.
Define the term 'amorphous' Give some examples of amorphous solids.
Classify the following solids into different types:
Plastic
What is a glass? Distinguish between crystalline solids and amorphous solids. Give examples.
Explain crystalline solids and amorphous solids.
Give the classification of solids.
Explain the terms isomorphism, polymorphism, anisotropy and unit cell.
Find the simplest formula of a molecule in which 'A' atoms are present at each corner and 'B' atoms are present at each edge centre of a truncated octahedron
The arrangement ........is referred as
The ability of a given substance to assume two or more crystalline structure is called
Which of the following is not a crystalline solid ?